Mosquitoes are a common flying insect that are found throughout the world. There are 3,500 different types of mosquitoes. They can be a nuisance, especially during hot weather as many of them bite, leaving an itchy bump on your skin. Mosquitoes bite animals and people to get a blood meal. The females need this blood in order to produce eggs.
There are mosquitoes that, when they bite people or animals, spread germs like viruses and parasites. They are called vectors. Vectors spread disease and germs that will make the person bitten sick.
Some mosquitoes are called nuisance mosquitoes as they bite, but do not spread germs and disease. (One would think that all mosquitoes are a nuisance, especially in humid weather.)
What happens when a mosquito bites you?
A mosquito will bite you if she is looking for a blood meal. Only female mosquitoes bite to get this. Male mosquitoes do not bite animals and neither do they bite humans.
If a female mosquito bites you, she pierces your skin using her proboscus – her mouth part – to suck up the blood. While she is feeding, her saliva is injected into your skin. Your body will more than likely react to the saliva and form a small bump along with itching.
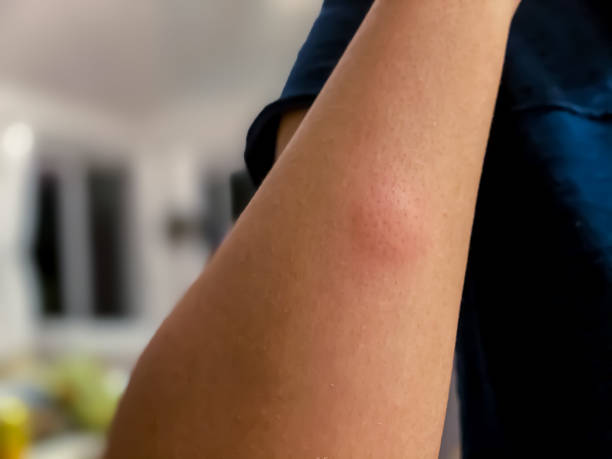

If a mosquito bites you, you’ll notice a small reddish bump, sometimes with a dot in the middle, within minutes. Most mosquito bites are not painful when they happen, where only a mild pinprick is felt. The bump starts to itch, especially in hot, humid weather, or if you touch or scratch it.
A mosquito bite is not a serious health condition. A person can have a reaction to a mosquito bite that causes swollen glands, a mild low-grade fever and red, itchy spots around the area of the bite. Generally though, a mosquito bite is painless with little consequences.
It is when a person is bitten by a mosquito that is carrying a disease that it becomes a problem.
Read our popular article – Allergies Overview: Symptoms , Causes and Types
Mosquito-borne diseases
First, more about vectors:
A vector is a living organism that can pass on an infectious pathogen from human to human, or from animals to humans. Mosquitoes are disease vectors, in particular, female mosquitoes. As a blood sucking insect, it ingests a disease producing microorganism during a blood meal from an infected host. The host can be either human or animal.
The mosquito transits the disease into a new host after the pathogen has been replicated. A vector, once it is infectious, can transmit the pathogen for the rest of its life during each blood meal it has. In total, a mosquito lives for 1 to 2 months.
Onto different mosquito-borne diseases…
These include diseases called malaria, dengue, West Nile virus, chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika.
Malaria
This is a serious and sometimes fatal disease. It is caused by a parasite that infects a particular type of mosquito that feeds on humans. Only the Anophelesmosquito can transmit malaria. Additionally, they must first be infected through a blood meal taken from an infected person.

When a mosquito bites an infected person, a small amount of blood is taken in which contains microscopic malaria parasites. Roughly 1 week later, when the mosquito takes its next blood meal, these parasites mix with the mosquito’s saliva. They are then injected into the person being bitten. Malaria cannot be transmitted from human to human.
People who get malaria are typically very sick with high fevers, shaking chills, and flu-like illness. About 2,000 cases of malaria are diagnosed in the United States each year. Most of the cases of malaria in the United States are in travelers who are returning from parts of the world where malaria transmission occurs.
Malaria typically occurs in more than 100 countries across the world. These include large areas of Africa and Asia, Central and South America, Haiti and the Dominican Republic, some parts of the Middle East and a few Pacific Islands.
Dengue
The Dengue virus causes Dengue fever. It is also transmitted by mosquitoes. The symptoms of this disease usually begin 3 to 14 days after infection. They can include a very high fever, headache, vomiting. Symptoms also include muscle and joint pains, as well as a characteristic skin rash.

Recovery from this illness generally takes 2 to 7 days. Unfortunately, Dengue fever can develop into dengue heamorrhagic fever which is a more severe form of the disease and includes symptoms like bleeding under the skin and non-stop vomiting.
In recent decades, the global incidence of dengue has grown dramatically, with around 40 per cent of the world’s population now at risk. Every year, approximately 25,000 people around the world die from dengue fever.
It is prevalent in the Americas, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and the Pacific Islands.
West Nile virus
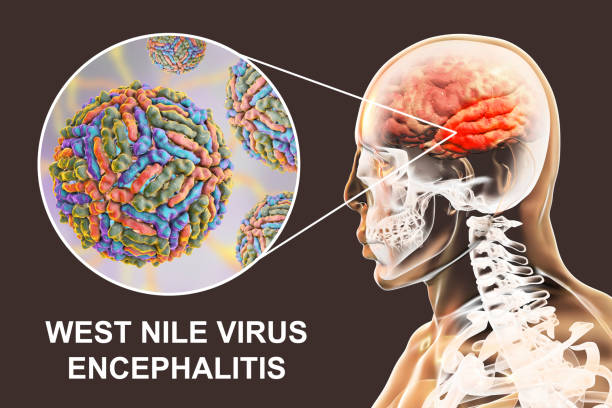
This is mostly caused by mosquito-transmitted West Nile infection. Birds are the natural hosts of this virus. Mosquitoes usually get infected when they feed on birds.
Most people who are infected with West Nile virus either don’t develop signs or symptoms or have only minor ones, such as a fever and mild headache. However, some people develop a life-threatening illness that includes inflammation of the spinal cord or brain.
It is commonly found in Africa, Europe, the Middle East, North America and West Asia.
Chikungunya
It is another viral disease that is transmitted to humans by way of infected mosquitoes. The mosquitoes that infect with this disease live in and around houses and bite during the day

Symptoms usually include fever, joint pain, headache, muscle pain, joint swelling and a rash. In most cases, a patient’s condition will improve within a week. However, occasionally the joint pain may last for months or even years. Chikungunya shares some clinical signs with Zika and dengue, leading to potential misdiagnosis in areas where these diseases are usually found.
It is typically found in Africa, Asia, Europe, and the Indian and Pacific Oceans. In late 2013, the chikungunya virus was found for the first time in the Americas on islands in the Caribbean.
Yellow fever
It is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. These different mosquito species live in different habitats – some breed around houses (domestic), others in the jungle (wild), and some in both habitats (semi-domestic).

The ‘yellow’ in the name refers to the jaundice that affects some patients. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains (particularly in the back) and headaches. Symptoms tend to improve within five days. However, approximately 30,000 people around the world die from yellow fever every year.
There is an extremely effective vaccine available that does protect against yellow fever. The vaccine is both safe and affordable. One dose of this vaccine is more than sufficient to provide sustained immunity as well as life-long protection against the disease.
Yellow fever is endemic in tropical areas of Africa and Central and South America.
Zika fever
It is also called the Zika virus disease, or just Zika, it is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that was first identified in Uganda in 1947 in monkeys. The mosquitoes that infect with this disease bite mainly during the day, unlike other mosquitoes that bite at dusk or in the evening.

Most times, there are no symptoms, but it can present in a similar way to Dengue fever. The symptoms of Zika may include fever, red eyes, joint pain, a headache and a maculopapular rash (one that it has both raised and flat skin lesions). If a woman is infected by this virus while she is pregnant, her child can have serious health conditions such as microcephaly – a defect where the child’s head is smaller than it should be for its age – as well as Guillain-Barre syndrome. Both of these can result in life-long disabilities.
It is typically from tropical Africa, Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. As the symptoms of Zika are similar to those of many other diseases, many cases may not have been recognized. It is likely that Zika outbreaks have occurred in many other places, but not been reported.

Even though mosquitoes are tiny, all of a few millimeters long, they could be regarded as the most dangerous animals in the world. The World Health Organization estimates that mosquitoes infect up to 700 million people a year and that they are responsible for the deaths of more than 2 million of those people who were infected.
Protection from mosquito-borne diseases
Preventing a mosquito bite is always more effective than trying to treat it, especially if you consider the potential seriousness of the diseases that can be transmitted during the bite.
It is best to cover up your skin when you are outdoors. Insect repellent is as important, if not more. Also consider using insect repellent when you are doing activities that naturally increase carbon dioxide emissions and bodily odors, such as exercising outdoors.(Mosquitoes are attracted to the scent of human sweat.)
Home
In your home, mosquito coils can be burned and offer some protection for approximately 6 hours. Always remember to never let water stagnate anywhere in and around your home. Additionally do a regular check, especially during the rainy season, for any water that has gathered in buckets, coolers or other containers where mosquitoes can breed. Empty them out regularly.
Change the water in the bird baths in your garden at least once per week.
Mosquitoes typically swarm toward your home in the evening. Make sure you have a physical barrier such as mosquito screens, doors or net windows. These will effectively mosquito-proof your home.
Sleep under a mosquito net in summer. Also, where possible, sleep in air conditioned rooms, as this reduces the risk of mosquito activity. In your home, use a fan to blow away mosquitoes before they have a chance to land on you and feed.
If you can find out where they are coming from, or where they may be breeding, half the problem is solved. Speak to a pest removal company for advice on how to eradicate their breeding area.

Traveling
If you are planning on traveling to a country that has high incidences of the mosquito-borne diseases, prophylaxis or vaccinations are available. Because infected men can pass Zika to their partners during sex, if your partner is pregnant or may become pregnant, and you will be in an area with Zika, ensure that a condom is used during sex to reduce the risk of infection.
When camping, sleep under a mosquito net. It is also a sensible idea to wear covered shoes when you are outside. Not only will this help protect your feet from being feasted on by a mosquito, it will also protect your feet from other nasty insect bites.
Nuisance insects, indeed
The number of people who have fallen victim to mosquito-borne diseases has risen dramatically over the past few years. Some scientists have postulated that it is because the earth is getting warmer and wetter. Mosquitoes love the heat and moisture. They are breeding more prolifically than they have before.
As worldwide travel is easy, a person visiting Africa can be bitten by a malaria-infected mosquito and only discover he is ill when he has left the continent and is back home.
Nevertheless, mosquitoes are a nuisance. They buzz in people’s ears, fly into the eyes, and bite the unsuspecting. While these ‘nuisances’ are tolerable, it is the diseases that they can spread that are the worry.
Taking the correct precautions against any potential mosquito bite can help save you from being infected with a nasty mosquito-borne disease.


